Polyploidy Is an Evolutionary Mechanism That May Result in
Speciation by polyploidy which is common in plants can cause a new species to form in one generation. Unreduced gametes gametes with the somatic chromosome number are known to facilitate polyploid formation.

Unreduced Gametes Meiotic Mishap Or Evolutionary Mechanism Trends In Genetics
Polyploidy though less common in animals than it is in plants appears to have played a role in the speciation in animals.

. Which of the following organisms is a primary producer. The presence of more than one set of homologous chromo- explicitly considered as a mechanism for evolutionary somes originating from different species within an organism. Polyploidy is characterized by ____.
In animals these abnormalities are usually lethal. Polyploidy arises as the result of total nondisjunction of chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis. Various mistakes that can occur during the biological processes of sexual reproduction can lead to offspring with abnormal numbers of chromosomes eg.
The evolutionary transition from diploidy to polyploidy is prevalent in flowering plants and may result in correlated changes in mating system outcrossing rate. This process is known as. Polyploidy is common in nature and provides a major mechanism for adaptation and speciation.
This pattern of missing ancestors may result from the short evolutionary life span of unisexual lineages or the selective advantages of polyploidy or it could suggest that alternative mechanisms of triploid formation are operating in nature. A condition in which one chromosome is present in three copies. Once united in a common nucleus genes duplicated by polyploidy may retain their independence and continue to evolve at equivalent rates as if they were localized in different diploid nuclei.
However the classic pioneering work of Clausen et al. It has been suggested that the rationale for this prevalence of polyploids is that it provides novel genetic and genomic variation that can allow polyploid individuals to exploit new environmental niches and outcompete their diploid progenitors 1. Unreduced gametes result from a plethora of different mechanisms across different taxa suggesting that the ability to produce unreduced gametes has.
The niche of an organism is the result of many years of natural selection. A surge in birth rates in mammals. Ernst Mayr the chief proponent of the biological species concept considered polyploidy one of the important mechanisms of speciation in the plant kingdom2 Subsequent authors concurred writing Polyploid speciation is instantaneous sympatric and may often involve population bottlenecks3 The population bottlenecks they mention occur because of.
The baldness trait becoming dominant in men. Polyploid plants have three or more sets of homologous chromosomes and have long been considered one of the main forces driving the evolution and diversification of angiosperms 1 2 3 4. Loss or gain of additional chromosomes relative to an established and within lineages for exaptive evolution a feature.
The evolutionary transition from diploidy to polyploidy is prevalent in flowering plants and may result in correlated changes in mating system outcrossing rate. Polyploidy is a prominent process in plants and has been significant in the evolutionary history of vertebrates and other eukaryotes 5 1012 4447. Speciation that should be measured and tested across Aneuploidy.
Epitomized the variety and array of ecogeographic diversity that can arise from whole-genome duplication. Unreduced gamete production may comprise an evolutionary mechanism for speciation. Asked Dec 31 2016 in Biology Microbiology by Crazy_Pride.
Polyploidy is believed to be a method for the origin of new species. In other words the polyploid cell or organism has three or more times the haploid chromosome number. Polyploidy is widely considered to be an enabling force in evolution.
A condition in which one member of a chromosomal pair is missing. Approximately 50-70 of angiosperms which include many crop plants have undergone polyploidy during their evolutionary process Chen et al 2007. Polyploidy is common among plants and has been in.
Polyploidy has been a common process during the evolution of eukaryotes especially plants leading to speciation and the evolution of new gene. This may explain why in the case of recent polyploids only few case of neo-functionalization have been reported while in ancient paleopolyploids such as Arabidopsis more duplicates have been. As a general rule species with a higher chromosome number are regarded more advanced than those with lower number from evolutionary point.
The failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis. In general when offspring end up having more chromosomes than normal this is called polyploidy. Broadly four outcomes emerged from.
Polyploidy can result in Sympatric Speciation. Most theory predicts a shift toward selffertilization decrease in outcrossing in polyploids but empirical evidence for this pattern and its underlying mechanisms is inconclusive or restricted to a few cases. Polyploidy involving the presence of multiple copies of identical or similar chromosome sets in one species is an important feature of species evolution in the plant animal and fungal kingdoms.
3N 4N or even more. Polyploidy the condition in which a normally diploid cell or organism acquires one or more additional sets of chromosomes. Numerous contending theories and results regarding polyploid distributions have filled botanical ecological and evolutionary journals for decades 237114116.
Another name for nutrient cycles in ecosystems is. Polyploidy is an evolutionary mechanism that may result in. Polyploidy is an evolutionary mechanism that may result in new plant species.
Most theory predicts a shift toward self-fertilization decrease in outcrossing in polyploids but empirical evidence for this pattern and its underlying mechanisms is. As this process involves selection of beneficial mutations Freeling 2008 neo-functionalization is a slow evolutionary mechanism Freeling 2009. Since evolutionists need an increase in information in the genome to go from molecules to man polyploidy is claimed to be a mechanism to increase genetic information available to a population.
See Glossary is prevalent across eukaryotic life particularly in the plant animal and fungal lineages. Polyploidy can lead to sympatric speciation because the polyploidy can result in different phenotypes with survival advantages that could allow them to occupyexploit different habitatsniches which can then lead to ecological isolation from the original organisms and so no gene flow between the polyploid and the original.
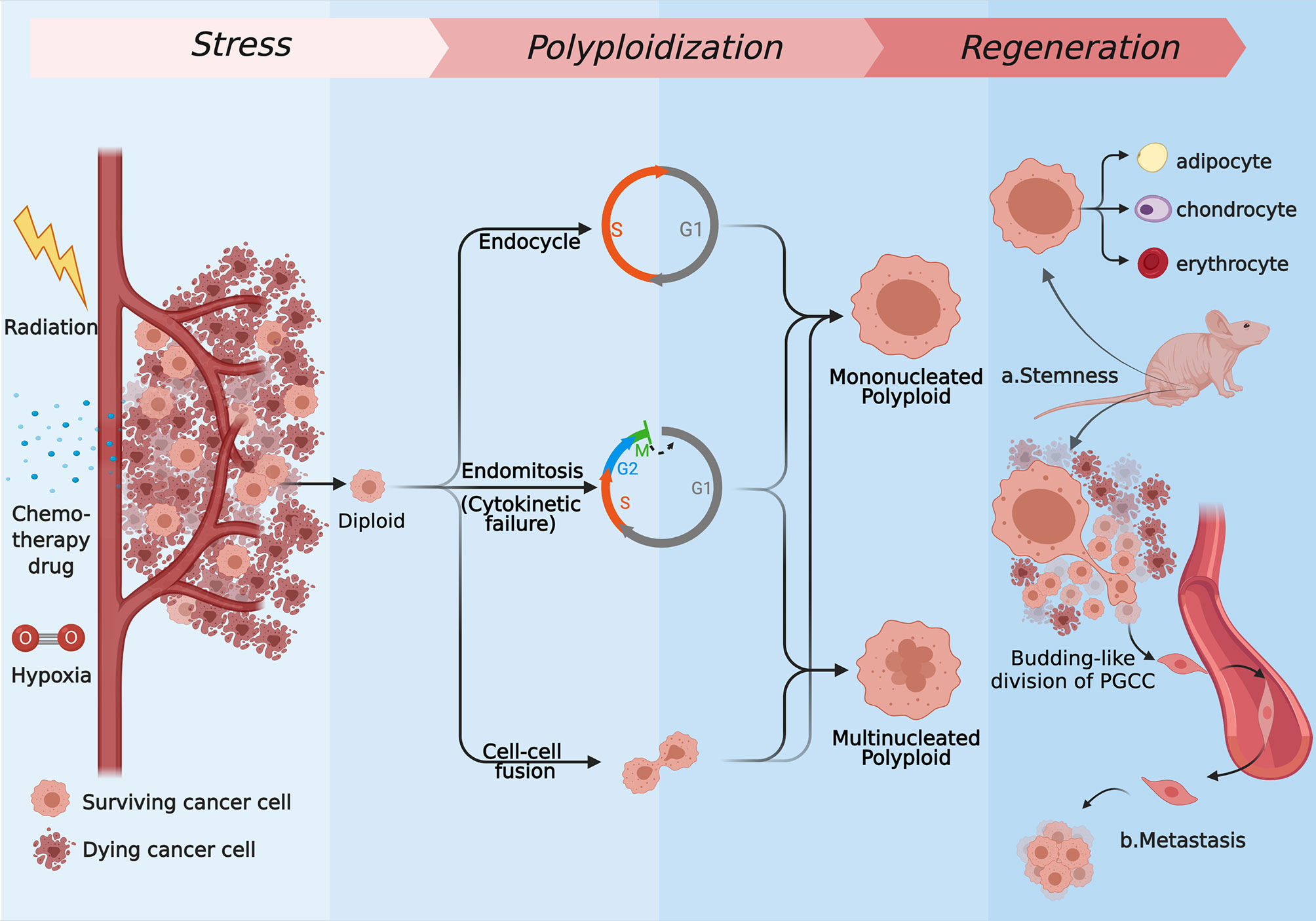
Frontiers Stress Induced Polyploid Giant Cancer Cells Unique Way Of Formation And Non Negligible Characteristics Oncology

Is Plant Polyploidy A Viable Mechanism For Evolution Answers In Genesis

Possible Pathways Of Allopolyploid Formation Polyploidy Can Be Download Scientific Diagram

The Evolutionary Consequences Of Polyploidy Cell

Polyploidy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Is Plant Polyploidy A Viable Mechanism For Evolution Answers In Genesis

Polyploidy The Nucleotype And Novelty The Impact Of Genome Doubling On The Biology Of The Cell International Journal Of Plant Sciences Vol 180 No 1
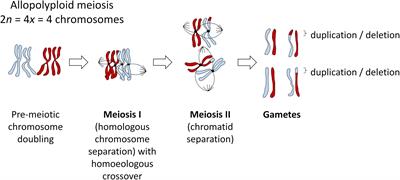
Frontiers Homoeologous Exchanges Segmental Allopolyploidy And Polyploid Genome Evolution Genetics
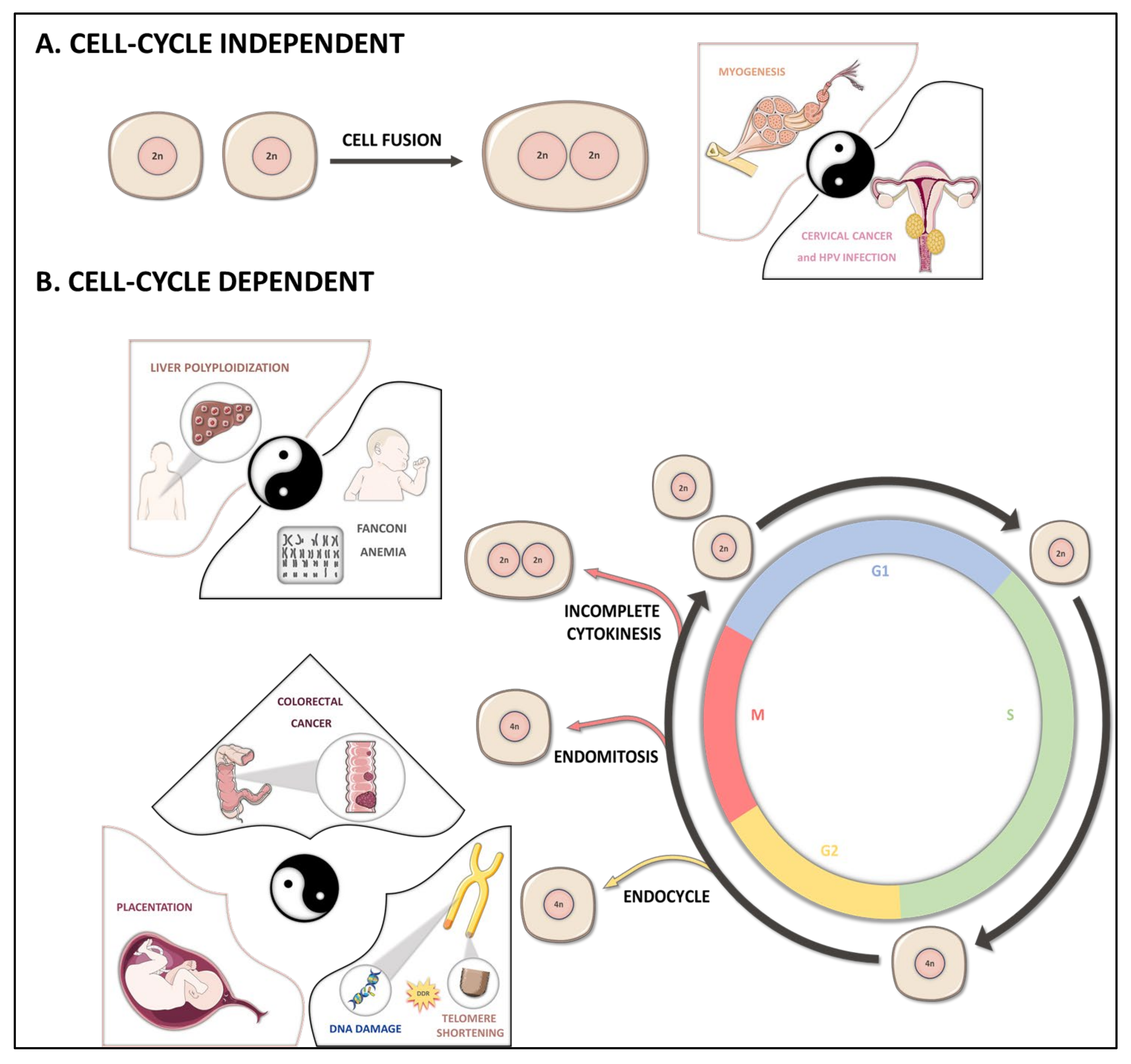
Cancers Free Full Text Hepatocyte Polyploidy Driver Or Gatekeeper Of Chronic Liver Diseases Html
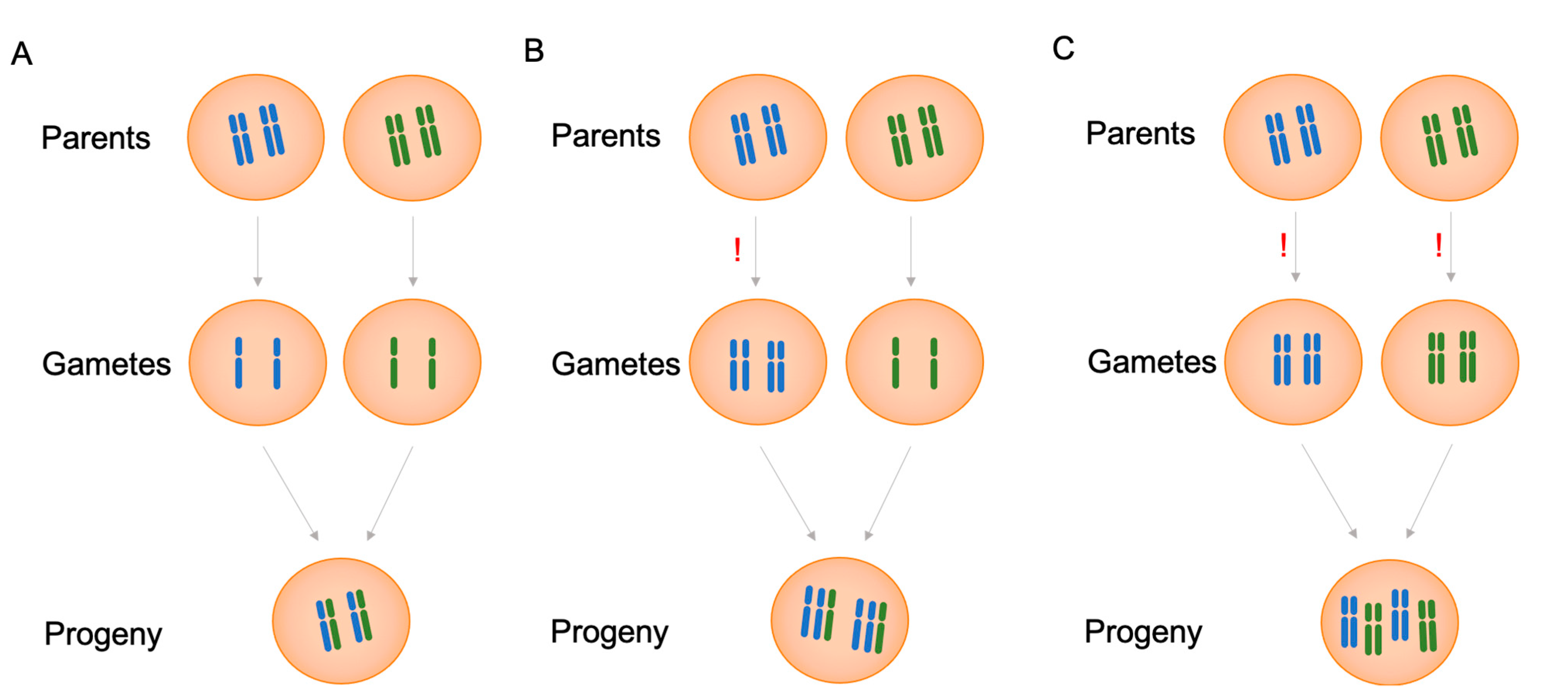
Biomolecules Free Full Text Effect Of Polyploidy Induction On Natural Metabolite Production In Medicinal Plants Html

Genomic Clues To The Evolutionary Success Of Polyploid Plants Current Biology

Genomic Clues To The Evolutionary Success Of Polyploid Plants Current Biology

Pdf Polyploidy And Genome Evolution In Plants

Is Plant Polyploidy A Viable Mechanism For Evolution Answers In Genesis

Polyploidy A Biological Force From Cells To Ecosystems Trends In Cell Biology
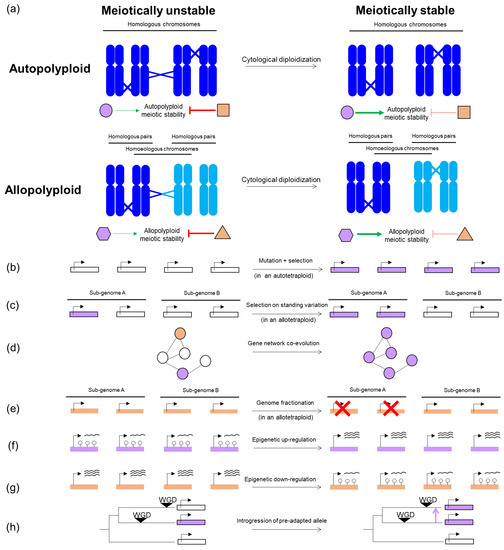
Genes Free Full Text All Ways Lead To Rome Mdash Meiotic Stabilization Can Take Many Routes In Nascent Polyploid Plants Html

Polyploid Evolution Keeping The Peace At Genomic Reunions Current Biology


Comments
Post a Comment